In today’s digital world, where every interaction with a website, app, or product matters, User Experience (UX) Design has become a cornerstone of successful digital strategies. But what exactly is UX design, and why is it so crucial? In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of UX design, its importance, and how it shapes our interactions with technology.
What is User Experience (UX) Design?
User Experience (UX) Design is the process of designing digital products and services that are not only functional but also enjoyable and efficient for users. It encompasses all aspects of the user’s interaction with a product, from the initial encounter to the ongoing use. The goal is to create a seamless, intuitive, and satisfying experience that meets users’ needs and expectations.
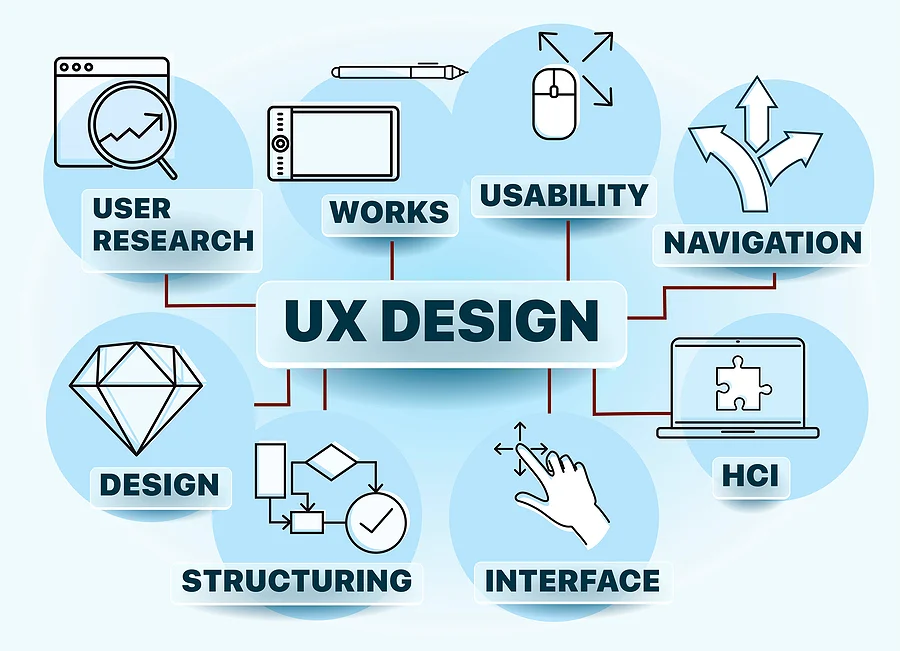
Key Components of UX Design
1. User Research:
- Understanding Users: Conducting research to gather insights about users’ needs, preferences, and pain points. This can include interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
- Personas: Creating detailed profiles representing different user types to guide design decisions.
2. Information Architecture (IA):
- Organizing Content: Structuring and organizing content in a way that users can easily navigate and find information. This involves creating sitemaps and defining navigation pathways.
3. Wireframing and Prototyping:
- Wireframes: Developing basic layouts to outline the structure of pages or screens, focusing on placement of elements and user flow.
- Prototypes: Building interactive models of the design to test functionality and gather feedback before the final implementation.
4. Usability Testing:
- Testing with Real Users: Observing users as they interact with the product to identify issues and areas for improvement. This helps ensure the design meets users’ needs effectively.
5. Interaction Design (IxD):
- Designing Interactions: Crafting the way users interact with the product, including buttons, gestures, and feedback. This ensures that interactions are intuitive and enhance the overall experience.
6. Visual Design:
- Aesthetics and Branding: Applying visual elements such as colors, typography, and imagery to create a cohesive and appealing look that aligns with the brand’s identity.
7. Accessibility:
- Inclusive Design: Ensuring that the product is usable by people with various disabilities, including visual, auditory, and motor impairments.
Why UX Design Matters
1. Enhanced User Satisfaction:
- A well-designed user experience makes interacting with a product pleasant and efficient, leading to higher user satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Increased Engagement:
- Intuitive designs keep users engaged and encourage them to spend more time with the product. This can lead to increased conversions and better user retention.
3. Reduced Costs:
- Investing in UX design early in the development process can save costs related to fixing usability issues and redesigning products later on.
4. Competitive Advantage:
- Products with superior user experiences stand out in a crowded market, giving businesses a competitive edge and fostering brand loyalty.
5. Positive Reputation:
- A product that provides a seamless experience enhances the overall reputation of the brand, leading to positive word-of-mouth and recommendations.
The UX Design Process
1. Research and Discovery:
- Gather information about the target audience, their needs, and the business goals. This phase sets the foundation for the design process.
2. Design and Prototyping:
- Create wireframes and prototypes based on research findings. Iterate on designs based on user feedback and testing.
3. Testing and Validation:
- Conduct usability tests to validate the design and make necessary adjustments. This ensures that the product meets user expectations.
4. Implementation:
- Collaborate with developers to bring the design to life. Ensure that the final product aligns with the design vision and maintains usability.
5. Evaluation and Iteration:
- Monitor user interactions with the product and gather feedback. Continuously improve the design based on real-world usage and changing needs.
User Experience (UX) Design is more than just a buzzword; it’s a critical aspect of creating products that resonate with users and achieve business goals. By focusing on understanding users, designing intuitive interactions, and continuously iterating based on feedback, UX designers play a vital role in shaping digital experiences that are both functional and delightful. In a world where user expectations are continually evolving, investing in UX design is not just beneficial but essential for creating successful and impactful digital solutions.
Get your development process with Smart Choice